Mitigation of Heat Stress by Probiotics

Probiotics as Mitigators of Heat-Induced Oxidative Damage in Poultry
More recently, probiotics have attracted considerable attention in subsiding oxidative damage caused by heat stress in poultry. Numerous researchers have reported the potential benefits of probiotics in improving gut morphology and integrity in heat-stressed birds.
Bacillus is of industrial importance for several reasons, including its excellent safety record, rapid growth rate resulting in short fermentation cycles, and ability to secrete proteins into the extracellular medium. Bacillus-derived peptides have been shown to have antifungal, antibacterial, antitumor, antiviral, anti-amoeba, and anti-mycoplasmic activities. Several species of Bacillus, such as Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus clausii, have been used as probiotic supplements in animal diets. A study reported that dietary probiotic supplementation reduced oxidative stress's negative effects on semen quality and increased breast meat weight in chronic heat-stressed broilers.
The Impact of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on Poultry Diets
Among aerobic bacterium Bacillus subtilis is one of the most crucial with beneficial effects on poultry diets by inhibiting the growth of aerobic pathogens, thereby increasing the efficiency of dietary protein in poultry. Bacillus subtilis has an enhanced potential to produce exogenous digestive enzymes, enhance intestinal development, improve immune responses and function, improve egg internal quality, and reduce egg yolk cholesterol concentrations. The facultative anaerobic bacterium, Bacillus licheniformis, has a beneficial effect on poultry diets by improving the intestinal absorption surface area and promoting the growth and proliferation of probiotics such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Aspergillus awamori.
In studies, Bacillus licheniformis was reported to maintain the goblet cell population in both the ileum and caecum of heat-stressed hens. It is therefore very important to state that dietary probiotics supplementation may be involved in preventing pathogens, improving nutrient absorption, and enhancing immunity, which ultimately translates into improved physical performance and disease resistance in heat-stressed poultry. The example of different types of probiotics and their application in poultry under heat-stressed conditions are shown in Table 1.
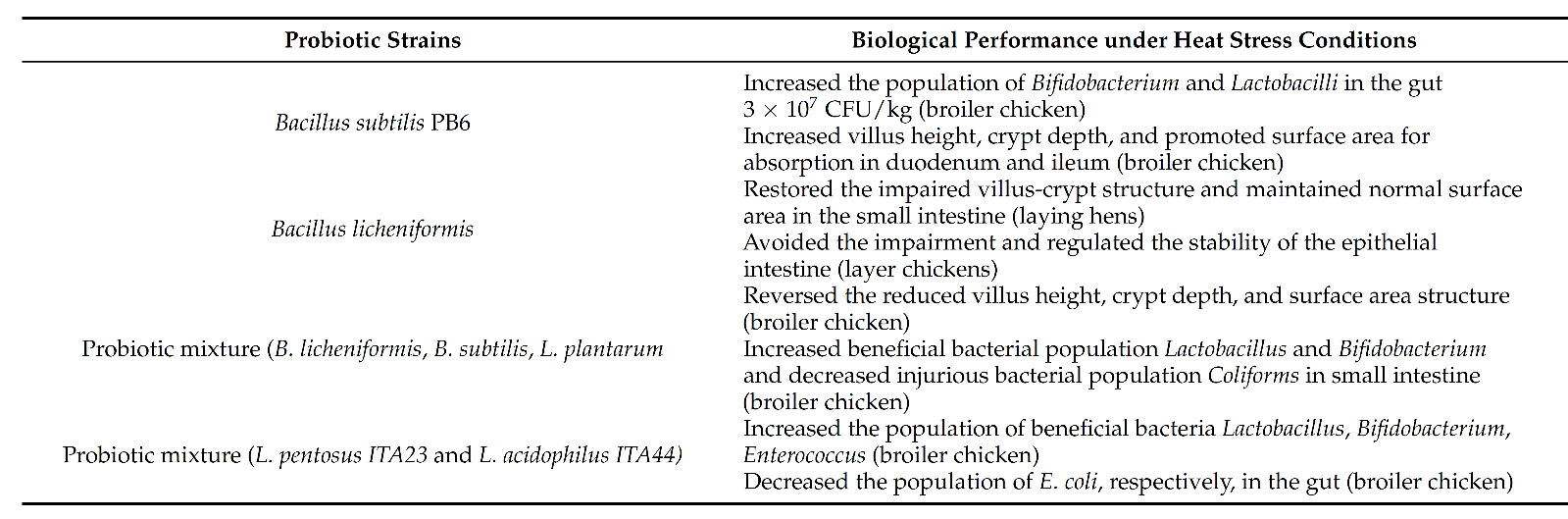
Table 1. Example of different types of probiotics and their application in poultry to ameliorate intestinal morphology under heat-stressed conditions.
Rising Temperatures, Rising Challenges
Heat stress has emerged as a serious threat to the poultry industry in many poultry-producing countries due to excessive increases in global temperature. Heat stress can affect poultry growth, gastrointestinal health, immune function, production status, and reproductive activity, thereby affecting poultry performance. Probiotics appear promising to mitigate detrimental effects in poultry raised under heat stress conditions, as probiotics can promote gut morphological activities, microbial ecology, physiological function, immune responses, and productivity in birds raised under heat stress conditions.Reference
Rafiq A, Yu Y. H., Hsiao S. H., Su C. H., Liu H. C., Tobin I., Zhang G. and Cheng Y. H. 2022. Influence of Heat Stress on Poultry Growth Performance, Intestinal Inflammation, and Immune Function and Potential Mitigation by Probiotics. Animals 12:2297
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- Combatting PEDV: How to Reduce Mortality and Protect Your Herd
- Strategic Care for Chicken in Cold Weather: Combating Poultry Viral Diseases
- Tired of Antibiotics in Shrimp Farming? Boost Gut Health & FCR with Advanced Postbiotics
- Understanding PRRS: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
- The Complete Guide to Sow Management and Feed Additives for Swine



